Generally speaking, food workers are only permitted to use designated handwashing sinks to wash their hands. Near areas where food is prepared and served, these sinks must be strategically placed. Food handlers are not permitted to use sinks used for janitorial tasks or sinks designated for food preparation. The same is true for kitchen appliances that are used for hand washing, such as brushes, soaps, and other tools.
Why is it essential that the food workers wash their hands? Read the article to find the right method to wash hands.
Table of Contents
Common Handwashing Sink Regulations
There are a number of rules regarding handwashing and related procedures in the FDA Food Code 2017 document. Each person who handles food must wash their hands at a sink designated solely for that purpose in accordance with the Food Code. A kitchen may have additional sinks for janitorial tasks, food preparation, and handwashing.
The FDA Food Code therefore specifies the following guidelines regarding the positioning, quantity, and necessary handwashing tools. Under the Food Code, handwashing regulations apply to the following:
- Hand Washing sink regulations for restaurants
- Hand Washing sink regulations for retail
- Hand Washing sink regulations for the commercial kitchen
Specifically, the FDA recommends every state in the US to adopt the following regulations:
- Food handlers are not permitted to wash their hands on sinks used for preparing food, only in designated handwashing sinks.
- Hand soap and hand antiseptics that have received FDA approval must be offered.
- The sink must be made so that it is simple to clean, along with the other plumbing fixtures.
- A minimum water temperature of 100°F (38°C) must be available at the handwashing sink. By using a mixing valve, this is possible.
- Restaurant restrooms and areas within 25 feet of the area where food is prepared must both have handwashing sinks available.
- Automatic faucets must have a continuous flow of water for at least 15 seconds.
- It is necessary to have paper towels available nearby the sink, either in individual or continuous towel systems. Alternately, a hand drying device with an air-knife system or an electric hand dryer can be installed.
- Unless otherwise specified by your local health department, a restaurant must have at least 1 handwashing sink that is required for the convenience of its staff.
- All sinks with handwashing facilities must have signage reminding users to wash their hands.
- Never allow a piece of portable cleaning equipment, dirty utensils, or other obstructions to block a handwashing sink.
- For temporary food establishments with insufficient access to a sink and water source (such as food trucks), food handlers can use chemically treated wipes for handwashing.
A handwashing sink’s requirements may change depending on the approved food safety laws and regulations that your local authority is putting into effect. Due to the fact that the location of your sink, which has a big impact on the design of your kitchen, is one such specific instruction, it would be most convenient to consult them.

Why is It Essential That the Food Workers Wash Their Hands?
To stop the spread of pathogens that cause foodborne illness in a food establishment, handwashing is both the easiest fix and the most important step. The effectiveness of proper handwashing in lowering the risk of contracting food-borne illnesses has already been demonstrated in numerous reports. In fact, the CDC has given this initiative such high priority that they believe regular hand washing would prevent at least 1 million deaths annually. It is the best line of defense against tainted food.
One of the main sources of dangerous pathogens is known to be the food industry. They are sources of these pathogens as well as vehicles for the spread of dangerous bacteria. Bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus, a known potent pathogen are considered an indicator of poor food hygiene and naturally live on different human body parts – mostly the skin.
More than just the food they prepare is held by food handlers. Additionally, each food handler touches aprons, doors, utensils, and other objects throughout the course of a shift. Food handlers are required to wash their hands before, during, and after food service as part of good food hygiene procedures.
You can help your team remember important food hygiene tasks such as handwashing and sanitizing contact surfaces with the help of our digital solution at We at FoodDocs have created a thorough digital food safety management system software that can assist you in always remaining compliant.
Where is a Sink in the Kitchen?

There must be a hand sink within 15 feet (in a straight line) of any area used for food preparation, one hand sink is needed for every five workers or every 300 square feet of workspace, and one hand sink is needed for each cooking and preparation area.
Place a hand sink as close as possible to the kitchen’s entrance and exit doors, as well as each prep area.
Items That Are Required at a Hand Wash Sink
As stated by the FDA (Department of Food and Drug Administration) in its Sec. 112,130, apart from water work personnel must be provided with soap and adequate drying devices (such as single service towels, sanitary towel service, or electric hand dryers).
This code also prohibits the use of antiseptic soaps in place of regular soap.
What You Should Look for in a Basic Hand Sink Selection?
- Pick a manufacturer with a solid track record in the food service industry.
- Use Type 304 stainless steel that has been shaped for improved strength and proper drainage.
- Consider using a “knee” hand sink where you don’t have to use your hands to open and close the faucet.
- Choose a sink with a deeper bowl for better drainage and splash guards to avoid cross-contamination.
- Choose a manufacturer that offers local technical support that is simple to access.
- Improved sanitation and sanitizing will result from seamless construction.
- Think about surfaces that are antimicrobial or that have a high degree of polish.
- It is preferable to select a stainless steel sink because it is durable and easy to clean. Type 430 and Type 304 stainless steel are typically used by manufacturers. Both are permitted for use in foodservice, but Type 304 is regarded as more durable due to the presence of nickel to some extent.
What is the Purpose of Hand Washing?
89% of foodborne illness outbreaks attributed to food handlers are caused by germs on hands. Your hands harbor germs even if you’re in good health. For instance, one in four people have staph bacteria in their noses or on their skin. The bacteria are typically harmless if they remain there. However, they can spread illness through food if they get into food and start to grow. Because of this, washing your hands is crucial!
The areas where food is prepared, served, and dishes are washed at your workplace should have handwashing sinks nearby or adjacent to them. Additionally, you need to have handwashing sinks in or near the restroom. Warm water, soap, paper towels or an air dryer, and a sign reminding workers to wash their hands are all required at handwashing sinks. If paper towels are provided at the handwashing station, there ought to be a trash can nearby to dispose of them in. If a handwashing sink runs low on supplies, let your manager know right away.
What is the Correct Order of Steps for Handwashing?
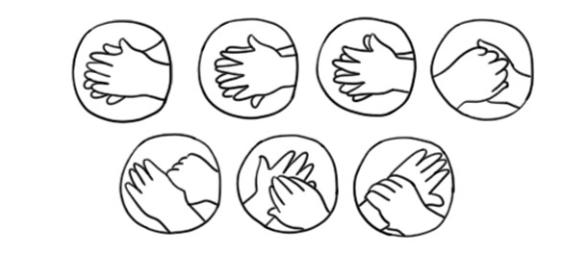
The six fundamental steps for washing your hands have been mentioned. To ensure that handwashing is effective, additional more specific actions must be taken in addition to these fundamental ones. All edges of the soap lather must be used when washing your hands. When necessary, you can also use a soft brush to dislodge dirt. When handling ingredients that stick to their hands, such as flour when kneading dough, food workers may need to use a brush.
Specifically, we encourage you to wash your hands using these easy steps:
- Step 1: wash your hands.
- Step 2: soap up your hands.
- Step 3: Groom your hands palm to palm.
- Step 4: Rub your hands together.
- Step 5: Rub your fingers together.
- Step 6:The thumbs’ bases should be rubbed.
- Step 7: Scrub your fingers’ nails (Note: You can also use a soft-bristled brush.)
- Step 8: Wash wrists.
- Step 9: Rinse hands thoroughly.
- step 10: Hands should be dried with a fresh towel or tissue.
- Step 11: Use a single-use paper towel to close the faucet.
In this series of handwashing procedures, you’ll notice that soap is applied to all corners of the hands before being washed. Food handlers’ nails can become a barrier for microorganisms, and they can even grow there. Additionally, some individuals neglect to wash their wrists as well. Each of these locations is crucial because it can allow pathogens to remain and possibly recontaminate hands.
Also, keep in mind that people who handle food are only permitted to dry their hands with clean towels or tissues. Recontamination of food handlers’ hands is more likely when hand dryers are used. In order to prevent their freshly cleaned hands from picking up any pathogens from the faucet, they must also refrain from touching the faucet with them. Instead, they must use a clean piece of paper towel.
Use one of FoodDocs’ food safety posters to help your team remember each step in the correct handwashing procedure.
When Food Handlers Should Wash Their Hands?
Hands should be washed as often as necessary and always:
- Before putting on gloves
- After handling raw meat
- After coughing or sneezing
- After touching your skin or hair
- After eating, drinking, or using tobacco
- After touching dirty equipment and utensils
- After you use the bathroom, both in the bathroom and again when you return to your work area.
FAQs
What is Double Handwashing?
When using the restroom, food employees must always wash their hands in the sink and then again at a hand washing sink before returning to their jobs. This practice is called double handwashing.
How Should Food Workers Protect Food from Pathogens on Their Hands?
To prevent this: Wash hands with soap and hot water before and after handling food, and after using the bathroom, changing diapers; or handling pets. To clean up spills or kitchen surfaces, use paper towels or clean cloths along with hot, soapy water.
How Should Food Workers Protect Food from Contamination After It is Cooked?
Use hot, soapy water and paper towels or clean cloths to wipe up kitchen surfaces or spills. Use the hot cycle of your washing machine to frequently wash cloths. After preparing each food item, wash your cutting boards, dishes, and counter tops in hot, soapy water before moving on to the next one.
Where Can a Food Worker Wash Her Hands on a Utility Sink Or Bathroom Sink?
The areas where food is prepared, served, and dishes are washed at your workplace should have handwashing sinks nearby or adjacent to them. Additionally, you need to have handwashing sinks in or near the restroom.
Where Are You Allowed to Wash Your Hands Quizlet?
The rules state that food employees must clean their hands in a handwashing only sink or an approved handwashing facility; these sinks must have a sign or poster that states the sinks are designated for handwashing only.
Can a Food Worker Wash Her Hands in a Service Sink?
Wet wipes, hand antiseptics, or gloves are not a replacement for washing your hands. Use only the sinks designated for handwashing when washing your hands. Do not wash your hands in utensil, food preparation or service sinks.
Read about
- How To Ask A Coworker Out Without Making Awkward?
- Your Newest Coworker Is Not As Productive: What Should You Do?



